Mail Accounts
The Mail > Accounts page is where you create and manage mailbox accounts for your hosted mail domain(s) using a classic mail server/provider model. This part of MSPControl is designed for simple hosted mail platforms (for example, SmarterMail) where mailboxes, quotas, and mailbox-level features are managed directly on the mail system.
It provides a list view for quick administration (search, bulk enable/disable, and security toggles) and a detailed configuration form for each mailbox (password, mailbox size limits, identity fields, signature, autoresponder, and forwarding).
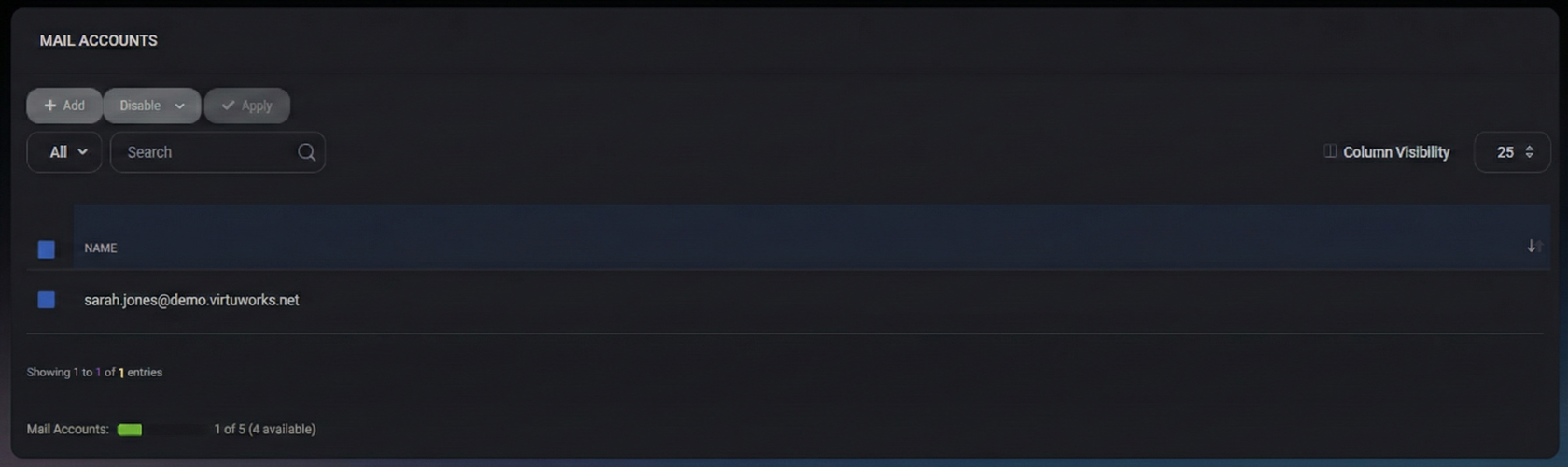
Table of Contents
Overview
Mail accounts represent individual mailboxes. From the list view you can:
- add new mailboxes
- enable/disable accounts in bulk
- toggle security-related settings (for example, email security)
- see capacity usage (how many mailboxes are currently provisioned vs available)
For detailed configuration (mailbox size, password, user identity, reply-to address, signature, autoresponder, forwarding), open the mailbox properties form.
Accounts List Page
The list page shows existing mailbox accounts in a simple table and includes standard table controls for search and navigation.
Displayed Columns
- Name – The mailbox address displayed as the unique identifier in the list.
List Controls
- View Filter (for example, All) – Switches between available list views if configured.
- Search – Filters the list by mailbox name/address.
- Column Visibility – Shows/hides table columns (useful if additional columns are enabled in other environments).
- Page Size (for example, 25) – Controls how many entries are shown per page.
Capacity Indicator
The footer displays mailbox capacity usage (for example: 1 of 5, with 4 available). Use this to confirm whether you can create additional mailboxes without increasing licensed capacity or plan limits.
The toolbar provides actions for creating accounts and applying bulk operations.
- Add – Starts creation of a new mailbox account.
- Disable (dropdown) – Opens the bulk actions menu for enable/disable and email security operations.
- Apply – Executes the selected dropdown action for all selected accounts. This is typically disabled until:
- at least one mailbox is selected, and
- a valid action is chosen in the dropdown.
Bulk Actions Dropdown
The bulk actions dropdown provides quick administrative controls for selected mailbox accounts.
Available Actions
- Disable – Disables the selected accounts so they can no longer be used for login/mail operations (depending on mail platform behavior).
- Enable – Re-enables previously disabled accounts.
- Enable Email Security – Turns on the mailbox-level email security option for selected accounts.
- Disable Email Security – Turns off the mailbox-level email security option for selected accounts.
How to Use Bulk Actions
- Select one or more mailboxes using the checkbox column.
- Open the dropdown (for example, Disable) and choose the action.
- Click Apply to execute.
Create a Mail Account
Use Add to create a new mailbox. This opens the mailbox configuration form (Mail Account Properties), where you define the address, password, mailbox size limit, and optional behaviors (signature, autoresponder, forwarding).
Mail Account Properties
The Mail Account Properties form is where you configure the mailbox identity and operational settings.
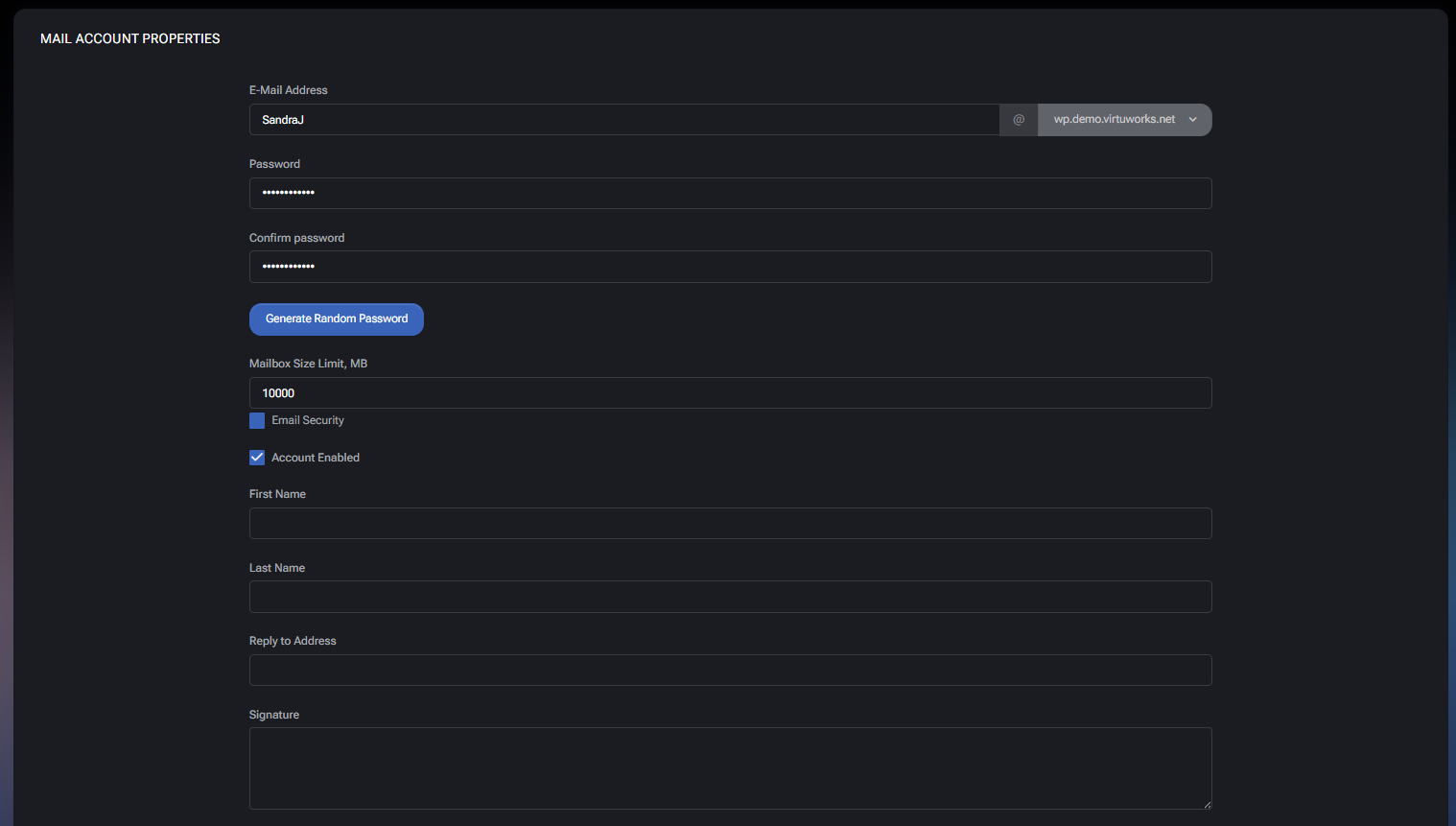
E-Mail Address
- Local part – The mailbox name (for example, SandraJ). Choose a consistent naming format to reduce duplicates and confusion.
- Domain selector – The domain portion (selected from a dropdown). This ensures mailboxes are created under the correct hosted domain.
Password
- Password – Sets the mailbox password.
- Confirm password – Ensures the password was typed correctly.
- Generate Random Password – Generates a strong password automatically. Use this when provisioning accounts to reduce weak-password risk.
Mailbox Size Limit, MB
- Mailbox Size Limit, MB – Sets the maximum mailbox size for this account. Use this to enforce quota policies, prevent a single mailbox from consuming excessive storage, and align usage with organizational standards.
Security and Status
- Email Security – Enables mailbox-level email security behavior. In simple mail providers (for example, SmarterMail), this typically maps to the provider’s mailbox security features (such as additional scanning, policy enforcement, or protections configured at the mail server level).
- Account Enabled – Controls whether the mailbox is active. Disable accounts when a user leaves the organization or during investigations, instead of deleting immediately.
User Identity and Mail Behavior
- First Name – Optional identity metadata for address books, display names, or organizational consistency.
- Last Name – Optional identity metadata.
- Reply to Address – Sets an alternative reply-to address. Use this when replies should be routed to a shared mailbox, ticketing system, or a different account.
- Signature – Default signature appended to outgoing messages (depending on client/mail platform behavior). Use it for standardized company signatures.
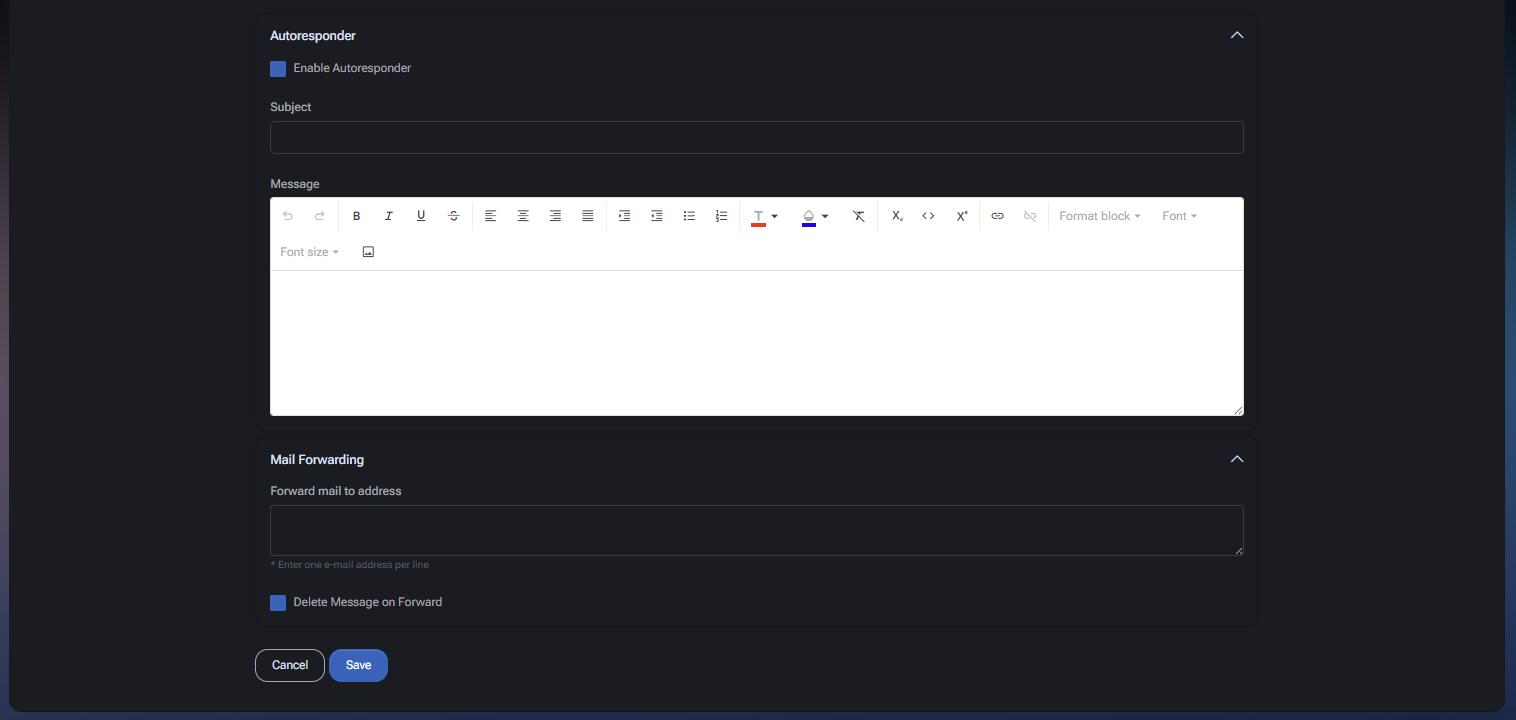
Autoresponder
The Autoresponder section allows the mailbox to automatically reply to incoming messages (for example, out-of-office, acknowledgements, or support routing messages). This is a standard mailbox feature supported by many classic mail providers (for example, SmarterMail).
Fields
- Enable Autoresponder – Turns autoresponder behavior on/off for this mailbox.
- Subject – The subject line used in the automatic reply.
- Message – The reply body, entered using a rich text editor (formatting, lists, alignment, links, and basic text styling).
Use autoresponder carefully for shared mailboxes and support addresses, because it can generate loops if it replies to automated senders. If your mail provider supports exclusions/loop protection, align autoresponder usage with your mail policy.
Mail Forwarding
The Mail Forwarding section forwards inbound messages to other address(es). This is commonly used for shared workflows, escalations, or ensuring continuity during transitions. Forwarding behavior is typically implemented by the underlying mail provider (for example, SmarterMail) and managed at the mailbox level.
Fields
- Forward mail to address – A multi-line field where you can enter forwarding recipients. Use one email address per line.
- Delete Message on Forward – When enabled, messages are removed from the original mailbox after forwarding. Use this only when the mailbox should act as a relay rather than an archive.
Actions
- Save – Saves mailbox settings (including autoresponder and forwarding).
- Cancel – Discards changes and closes the form.
Best Practices
- Use a standardized mailbox naming format (for example: firstname.lastname or department.role) to reduce duplicates and make administration easier.
- Prefer Generate Random Password for new accounts and rotate passwords for privileged/shared mailboxes regularly.
- Set reasonable Mailbox Size Limit values that match your organization’s storage policy and operational needs.
- Disable accounts using Account Enabled (or bulk Disable) when users leave, instead of deleting immediately. This protects continuity and auditability.
- Use Reply to Address for shared workflows (support, billing, operations) where replies must go to a central mailbox or ticketing pipeline.
- Be cautious with Autoresponder on shared/support addresses to avoid mail loops and automated reply storms.
- Only enable Delete Message on Forward when you explicitly want the mailbox to function as a relay and do not require mailbox-side retention.
- Use bulk actions (Enable/Disable, Email Security) for consistent policy enforcement across many mailboxes.





