Servers
In MSPControl, a Server represents a real machine—physical or virtual—where the MSPControl Server component is installed. By adding and configuring these servers in the MSPControl portal, you can manage the hosting services and resources they provide, such as web hosting, mail, FTP, databases, and more.

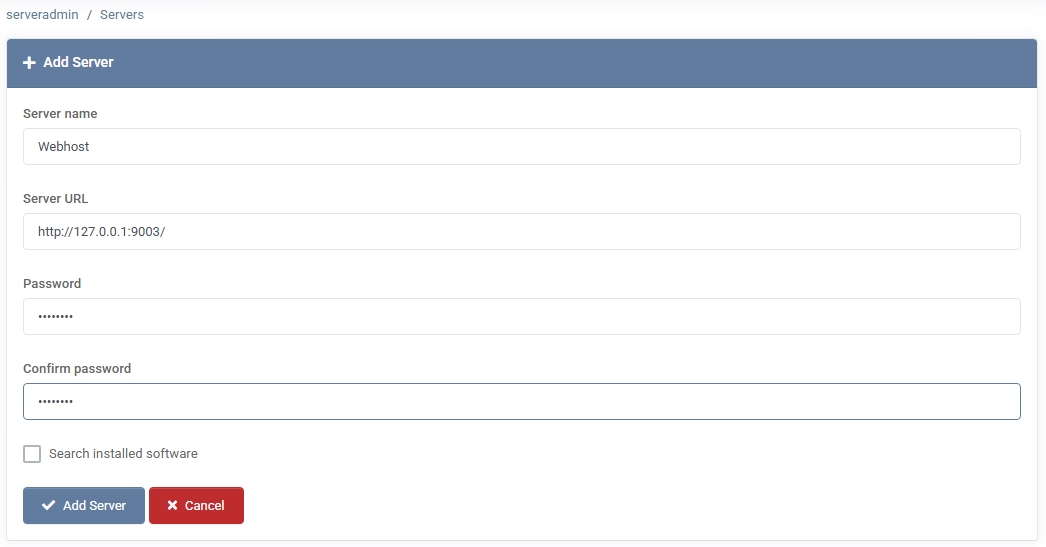
Adding a New Server
- Go to Settings > Servers
If no servers are listed yet, you’ll see an empty page. Click + Add Server.
- Server Name
Provide a clear identifier (e.g., “Webhost01” or “MailServerA”) so you can recognize it easily.
- Server URL
Enter the URL of the MSPControl Server component installed on the server you’re adding. For example: http://192.168.1.10:9002/ or https://hostname:9002/. MSPControl will use this address to communicate and manage services on that server.
- Password / Confirm Password
Enter the authentication password that was set during the MSPControl Server component installation, and re-enter it to confirm.
- Search Installed Software
(Optional) Enabling this option may let MSPControl automatically detect which services (IIS, Mail, SQL, etc.) are installed, simplifying subsequent configuration.
- Click “Add Server”
The server is now registered in MSPControl. You can then proceed to configure its properties and services.
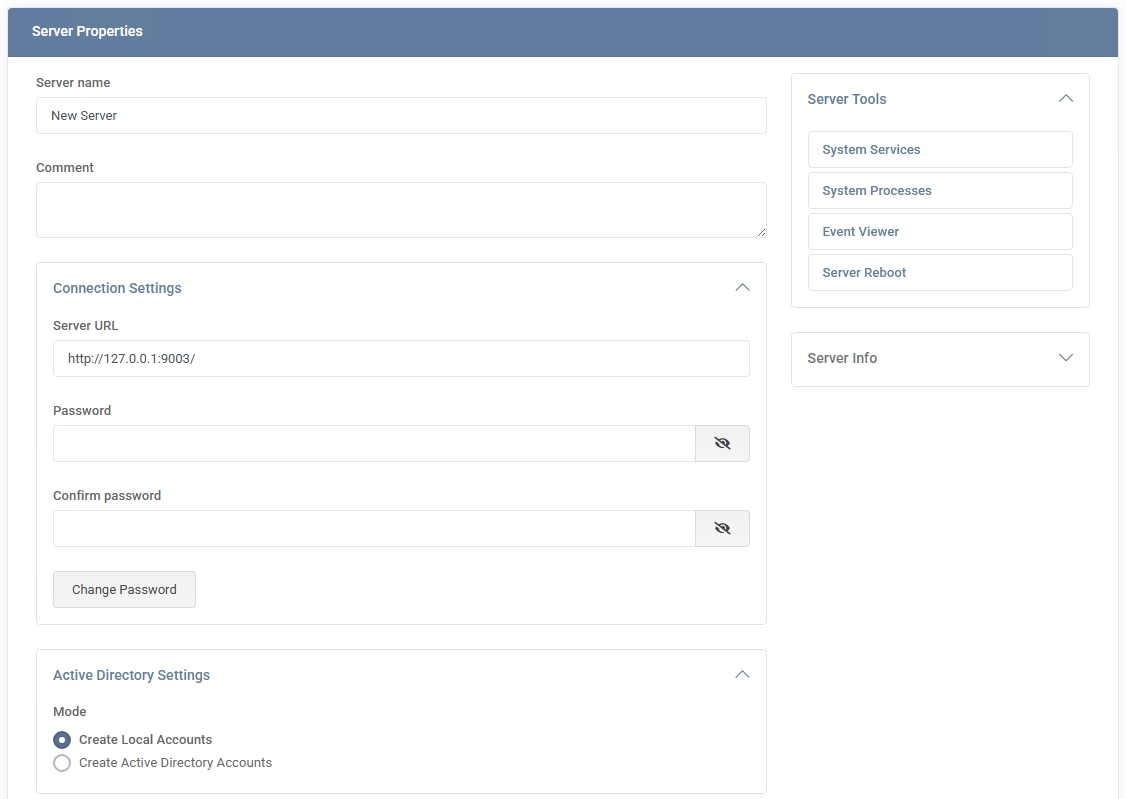
Server Properties
After adding a server, select it from the list to open its properties page, where you can:
- Change Server Name or URL – Update identification or connection settings if the server’s IP or domain changes.
- Configure Active Directory Settings – Decide whether to create local accounts or use Active Directory for user provisioning, and specify the domain details accordingly.
- Add IP Addresses – Define which IP addresses (and optionally NAT addresses or default gateways) are associated with this server.
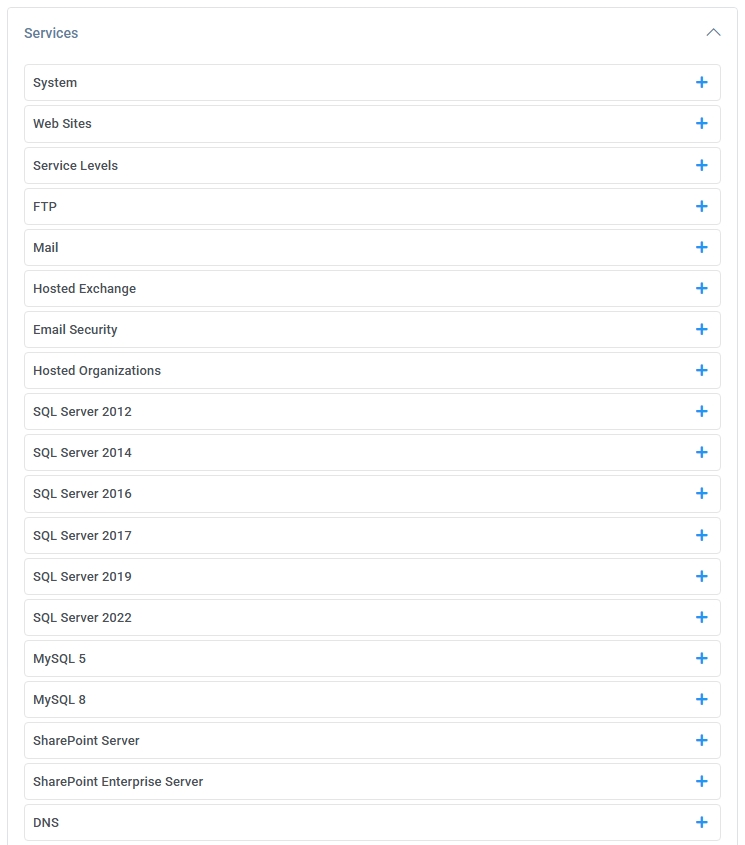
- Attach Services – Under the Services section (e.g., Web Sites, Mail, FTP, SQL),
configure or enable the corresponding service on this server.
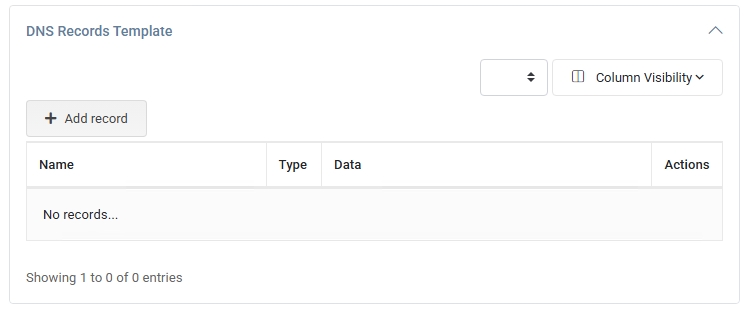
- DNS Records Template – If this server provides DNS services, add default DNS records (A, CNAME, MX, etc.)
that will be auto-generated for new domains.
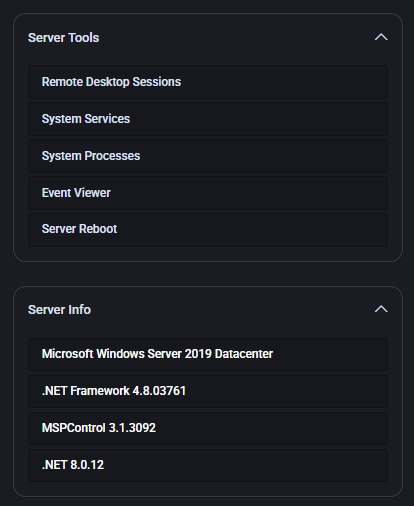
Server Tools & Info
On the right side of the Server Properties screen, you’ll find:
- Server Tools
– Remote Desktop Sessions: View and manage active RDP sessions (if supported).
– System Services: See a list of services running on the server, with options to start or stop them.
– System Processes: Monitor processes running on the server for troubleshooting performance issues.
– Event Viewer: Access Windows Event Logs for error tracking and diagnostics.
– Server Reboot: Initiate a remote reboot (where permissions allow).
- Server Info
Displays key system details, such as the operating system version, .NET Framework versions, and the installed MSPControl version.
This helps you quickly confirm the environment’s configuration for support or upgrade planning.
Adding Services
Once the server is recognized, you can attach specific services to it under the Services section.
This allows MSPControl to utilize the server’s capabilities when assigning hosting spaces or building out Virtual Servers that combine services from multiple real servers.
Next Steps
After setting up your servers, you can further enhance your hosting environment by:
- Defining Virtual Servers – Combine services from multiple real servers into a single logical “virtual server” for hosting plans.
- Building Hosting Plans – Use the servers (or virtual servers) to define resource allocations for customer hosting spaces.
- Configuring DNS Templates – If the server offers DNS services, set default DNS records for new domain creations.
Best Practices
- Use Descriptive Names – Choose clear, descriptive names for your servers to easily identify their roles (e.g., “Webhost01” for web services, “MailServerA” for mail services).
- Verify Connectivity – After adding a server, test the URL and credentials to ensure MSPControl can communicate with it successfully.
- Keep Server Information Updated – Regularly review and update server properties, such as IP addresses or DNS settings, to reflect any changes in your environment.
- Secure Access Credentials – Ensure that passwords and other authentication details are stored securely and updated periodically.
- Monitor Resource Usage – Use MSPControl’s monitoring tools to track the performance and load on each server, preventing resource bottlenecks.
- Leverage Automatic Service Detection – Enable the search for installed software to help automatically configure services, saving time and reducing errors.
- Regularly Review Security Settings – Check Active Directory and network settings periodically to maintain secure and efficient server operations.









