Hyper-V Policy
The Hyper-V Policy section in MSPControl allows administrators to configure provisioning and access rules for virtualized Windows environments. This policy includes two sub-sections:
Virtual Private Servers Policy and Remote Desktop Servers Policy. These settings ensure that users receive properly configured resources with consistent naming, security rules, and automation options.
Table of Contents
Virtual Private Servers Policy
This policy allows administrators to define secure password requirements, automatic VM start/stop behavior, and standard naming conventions for virtual machines hosted under Hyper-V. It ensures consistency and enhances security for VPS deployments across your infrastructure.
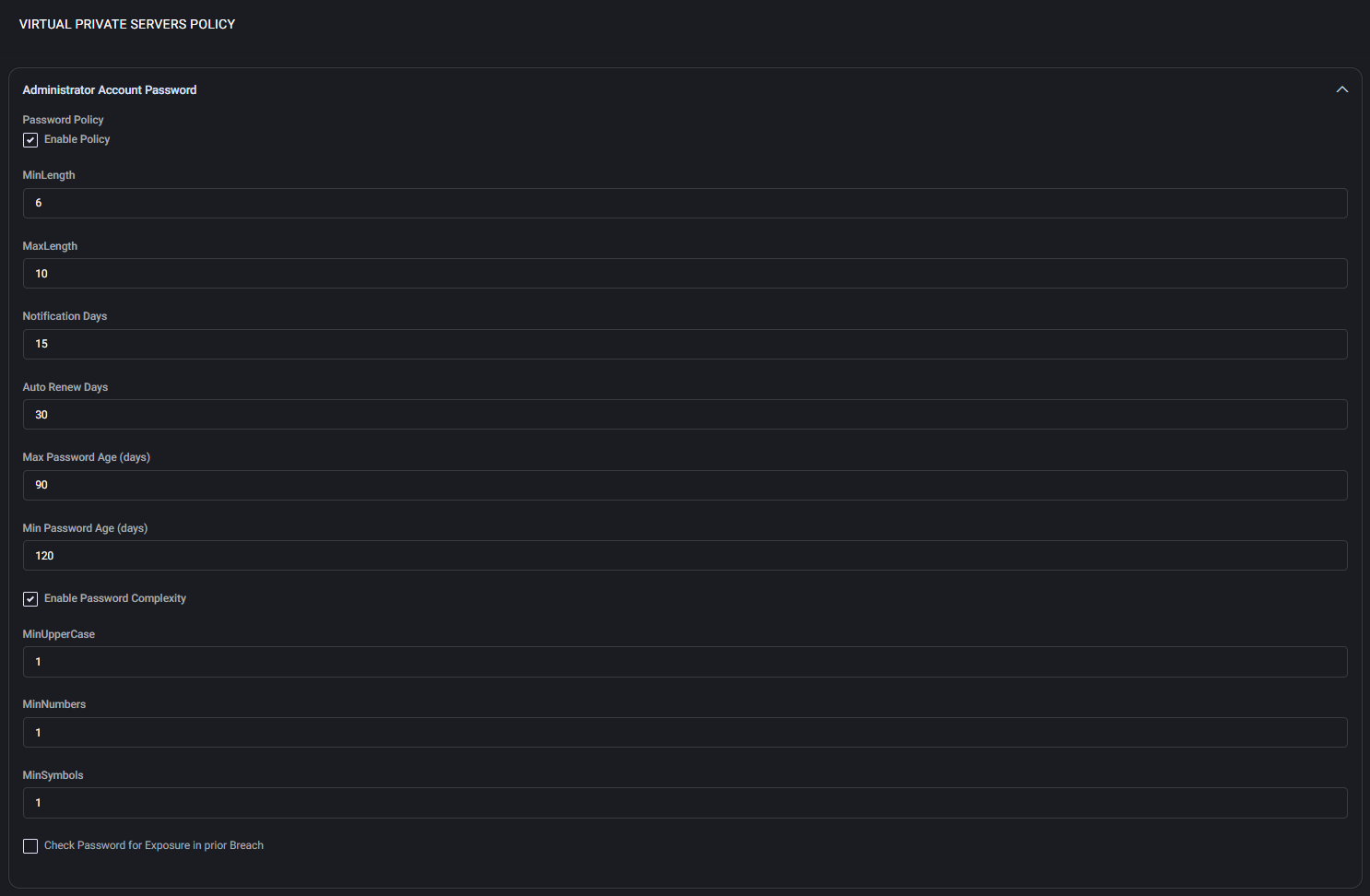
Administrator Account Password
This section enforces strong password policy rules for VPS administrator accounts:
- Enable Policy — Activates the entire password policy configuration.
- MinLength / MaxLength — Specifies the minimum and maximum allowed password lengths.
- Notification Days — Number of days before expiration to begin notifying the user.
- Auto Renew Days — Frequency of automatic password renewals.
- Max / Min Password Age — Defines password lifespan limits.
- Enable Password Complexity — Enforces complexity requirements:
- MinUpperCase: Minimum number of uppercase letters
- MinNumbers: Minimum number of digits
- MinSymbols: Minimum number of special characters
- Check Password for Exposure in prior Breach — When enabled, compares passwords against known breaches.
Processor Resource Settings
Controls CPU resource allocation for each virtual machine:
- Virtual machine reserve, % — Guarantees a minimum percentage of CPU resources.
- Virtual machine limit, % — Caps the maximum CPU resources available to the VM.
- Relative weight — Sets CPU resource priority relative to other VMs.
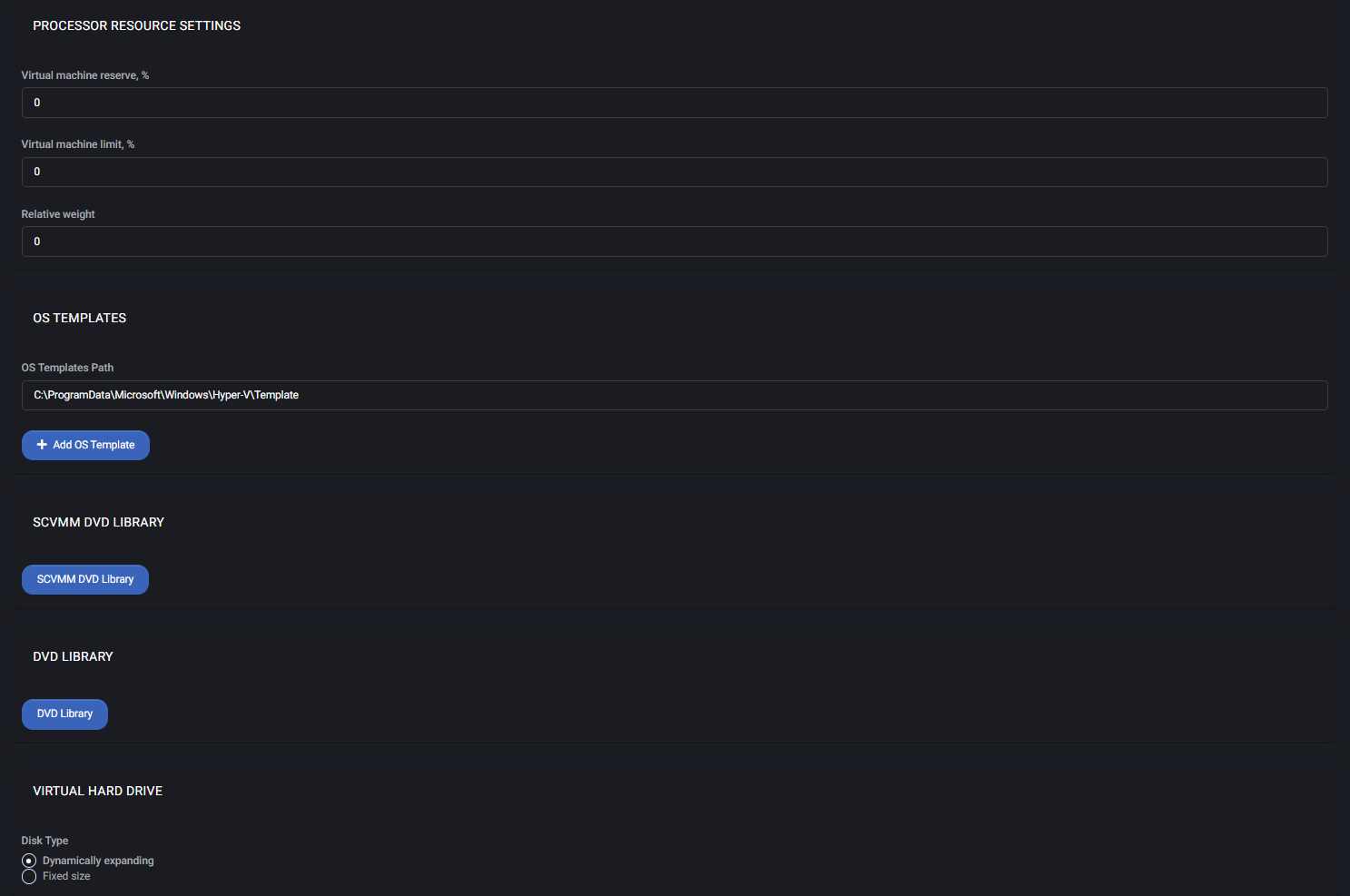
OS Templates
Specifies the path where operating system templates are stored for use during VM creation.
- OS Templates Path — The folder path used by Hyper-V to locate OS templates.
- Add OS Template — Allows you to upload and register a new template file for use.
SCVMM DVD Library
Provides access to the SCVMM (System Center Virtual Machine Manager) DVD library, enabling you to select ISO images stored centrally for VM deployment.
DVD Library
Specifies a custom DVD library location for loading ISO files directly within the MSPControl panel.
Virtual Hard Drive
Choose the type of virtual hard disk to use when creating virtual machines:
- Dynamically expanding — Starts small and grows as needed, saving disk space.
- Fixed size — Allocates the full size immediately, offering slightly better performance.
Virtual Machine Host Name
This setting configures a default pattern for hostnames of newly created VMs. If the user is not allowed to choose a custom name, the system generates it using:
[USERNAME]-[SPACE_ID]
Available substitution variables: [USERNAME], [USER_ID], [SPACE_ID]
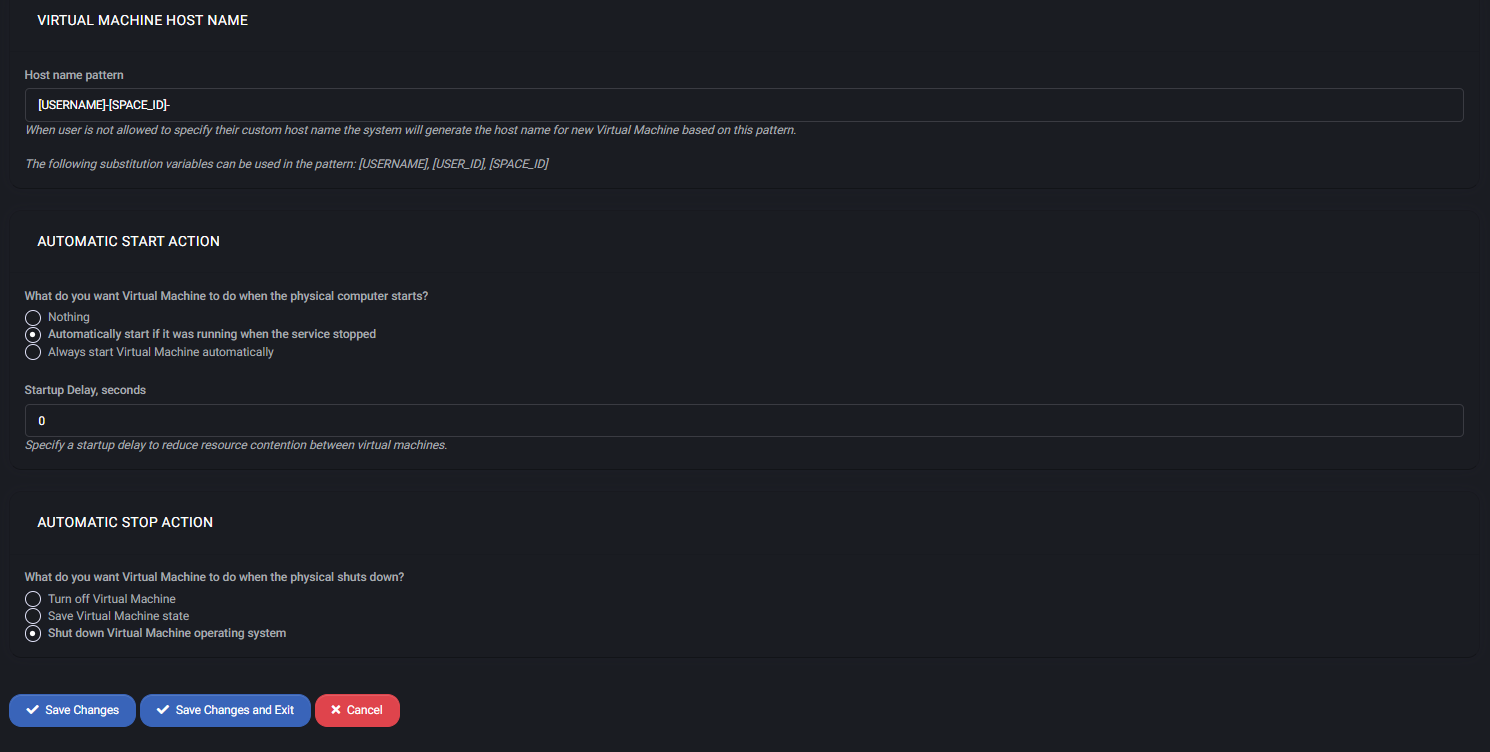
Automatic Start Action
Defines how the virtual machine should behave when the physical host restarts:
- Nothing — Do not start the VM.
- Automatically start it if it was running when the service stopped — Default option for restoring runtime state.
- Always start Virtual Machine automatically — Ensures VM always runs when host is up.
Startup Delay (seconds): Allows adding a delay to prevent resource contention during bulk startups.
Automatic Stop Action
Determines what should happen when the host machine shuts down:
- Turn off Virtual Machine — Powers off VM without saving state.
- Save Virtual Machine state — Pauses VM and stores memory state to disk.
- Shut down Virtual Machine operating system — Gracefully initiates an OS shutdown.
Remote Desktop Servers Policy
This section defines group-level restrictions and user experience configurations for Remote Desktop Servers provisioned under Hyper-V. It includes UI behavior, session control, security lockdowns, and default environment settings across four tabs.
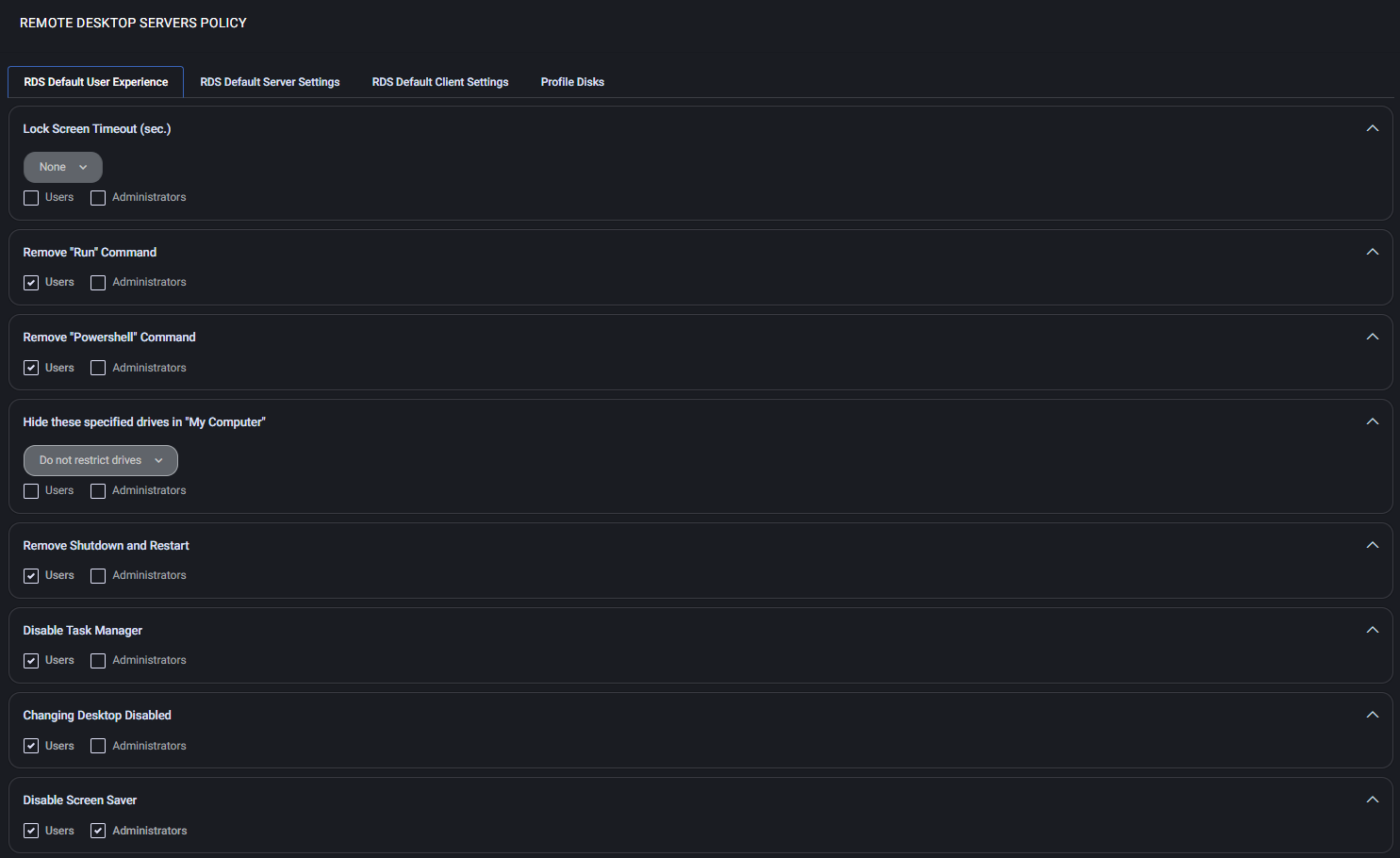
RDS Default User Experience
Customize what users and administrators can do during an RDS session. Each rule can be applied separately to Users or Administrators by checking the corresponding box.
- Lock Screen Timeout (sec.) – Set idle time before screen locks. Choose
None to disable timeout.
- Remove “Run” Command – Hides the Run option from the Start menu and taskbar.
- Remove “Powershell” Command – Prevents access to PowerShell from the UI.
- Hide these specified drives in “My Computer” – Choose which drives (A, B, C, D) to hide using a predefined dropdown. Available options include:
- Do not restrict drives
- Restrict A and B drives only
- Restrict C drive only
- Restrict A, B and C drives only
- Restrict D drive only
- Restrict A, B, C and D drives only
- Restrict all drives
- Remove Shutdown and Restart – Removes shutdown and restart options from the system menu.
- Disable Task Manager – Prevents access to Task Manager via shortcuts or context menu.
- Changing Desktop Disabled – Disables the ability to change desktop wallpaper or themes.
- Disable Screen Saver – Prevents screen saver from activating.
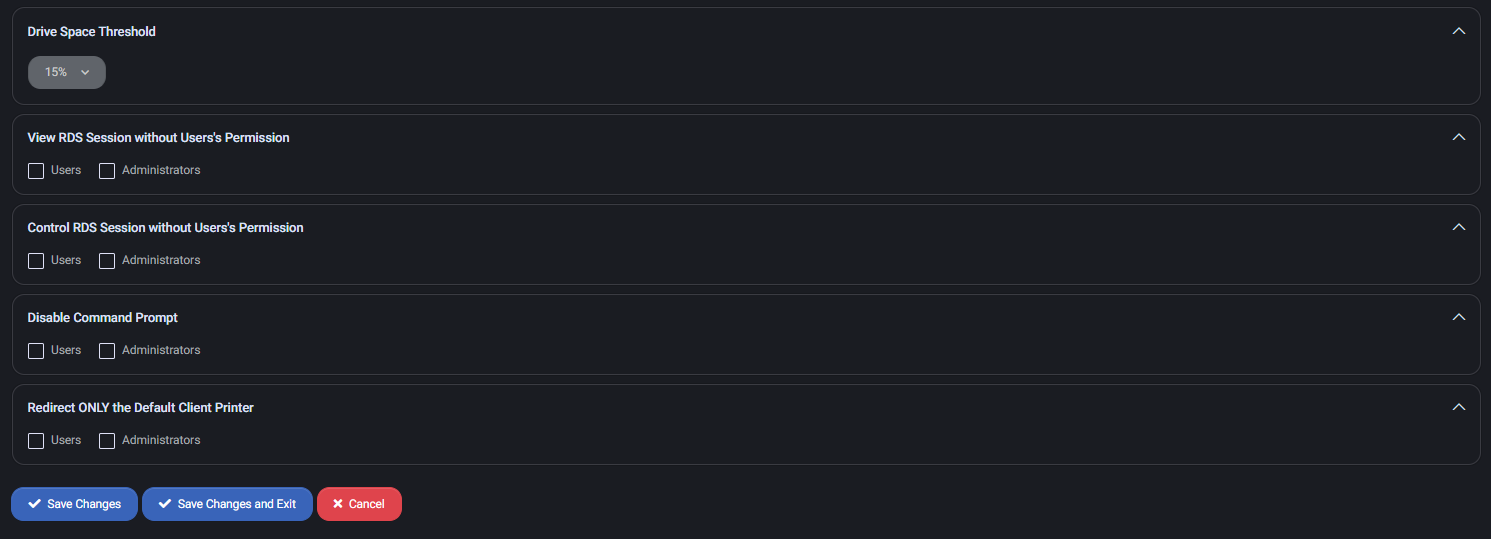
- Drive Space Threshold – Set minimum free disk space threshold (e.g., 15%) before warnings or restrictions trigger.
- View RDS Session without User’s Permission – Allow monitoring sessions silently.
- Control RDS Session without User’s Permission – Allow full control of sessions without prompts.
- Disable Command Prompt – Disables access to cmd.exe.
- Redirect ONLY the Default Client Printer – Prevents redirection of all printers except the default client printer.
RDS Default Server Settings
This tab defines how Remote Desktop Session Hosts manage connections, session limits, temporary folders, client resource redirection, and security requirements for RDS environments.
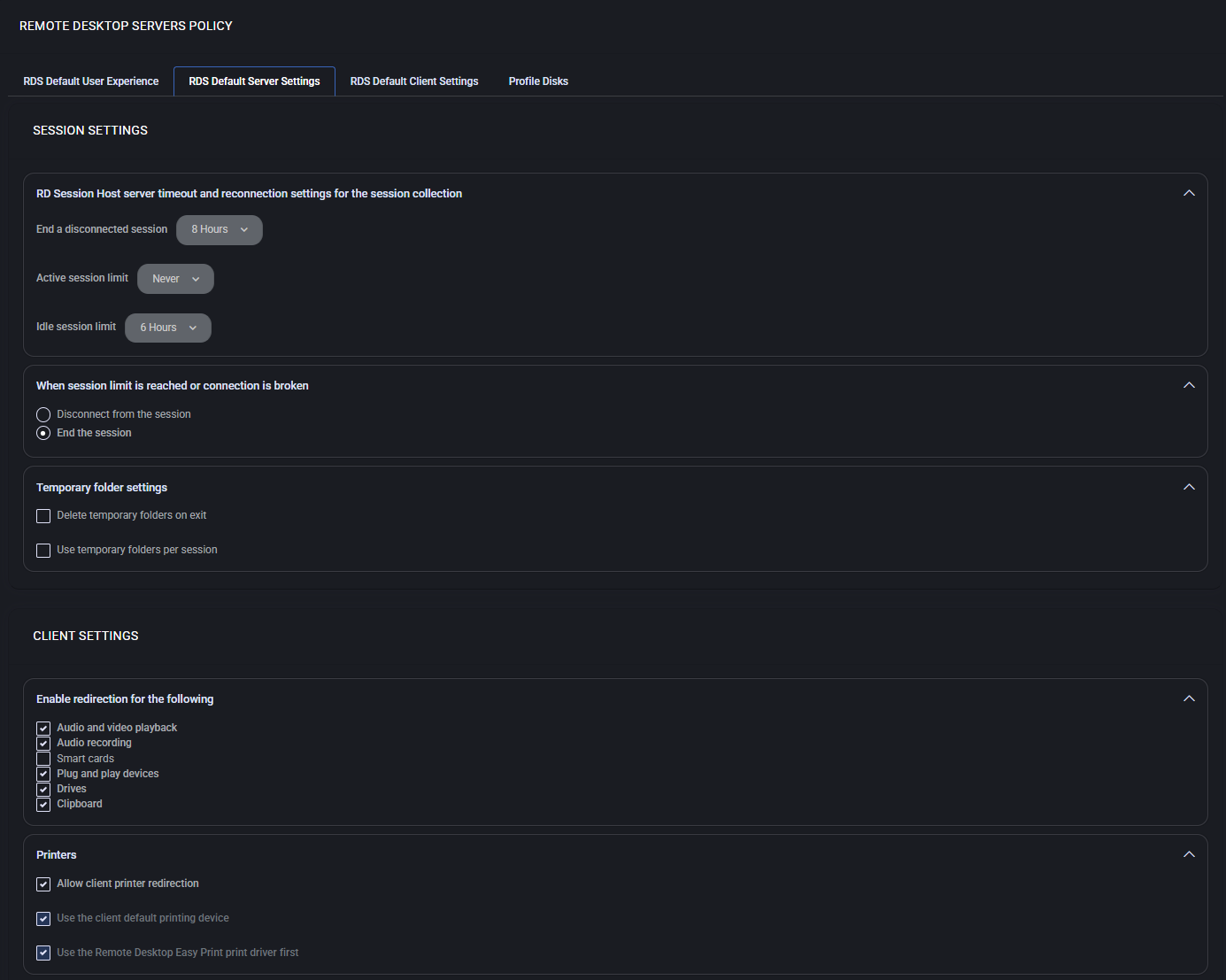
Session Settings
Controls how RD Session Host handles user sessions and reconnections in a collection.
- RD Session Host timeout: Defines how long a disconnected session remains active before being terminated (e.g., 8 Hours).
- Active session limit: Maximum time a session may run before being forcibly ended (e.g., Never or a defined period).
- Idle session limit: Ends sessions after specified inactivity duration (e.g., 6 Hours).
- When session limit is reached: Choose whether to Disconnect the user or End the session.
Temporary Folder Settings
- Delete temporary folders on exit: Cleans up user-specific temporary files when the session ends.
- Use temporary folders per session: Ensures each session has its own isolated temp folder, improving data separation and security.
Client Settings
Controls which client resources may be redirected into the RDS session.
- Enable redirection for: Allows specific features like audio and video playback, audio recording, smart cards, plug-and-play devices, drives, and clipboard to be redirected.
- Printers:
- Allow client printer redirection – Enables use of printers connected to the client device.
- Use the client default printing device – Sets the client’s default printer as the active RDS printer.
- Use the Remote Desktop Easy Print driver first – Prioritizes Easy Print for compatibility and reduced driver requirements.
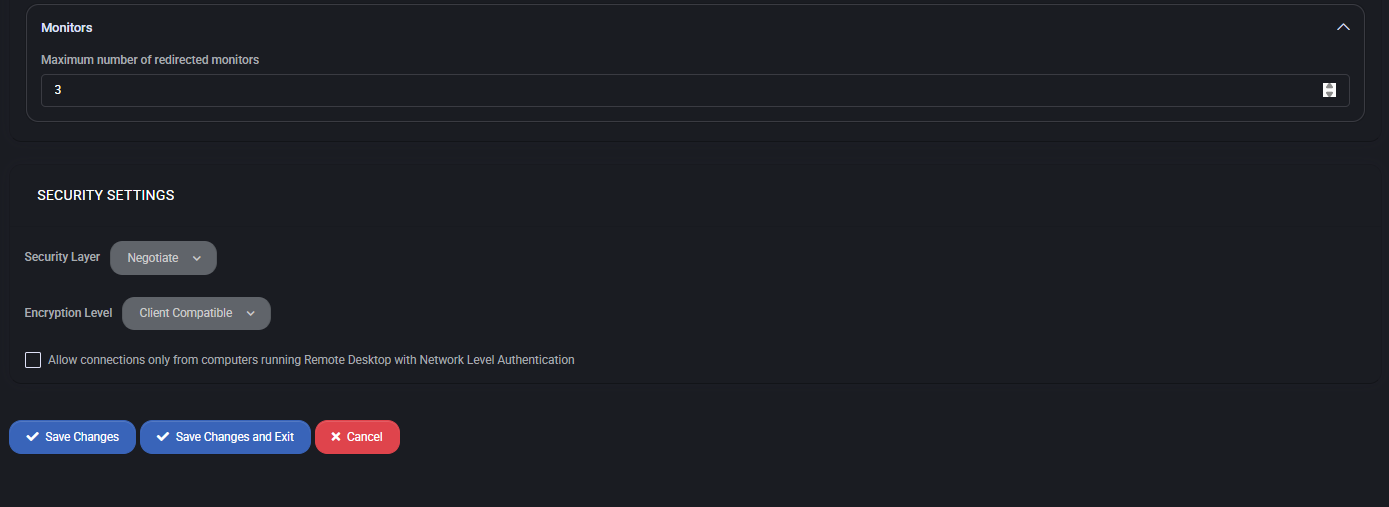
- Monitors: Defines the maximum number of redirected monitors supported (e.g., 3).
Security Settings
Defines encryption and authentication requirements for RDS sessions.
- Security Layer: Determines negotiation between RDP Security and TLS (default: Negotiate).
- Encryption Level: Sets the minimum encryption standard (e.g., Client Compatible).
- Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication: Enforces NLA for stronger authentication before a session is created.
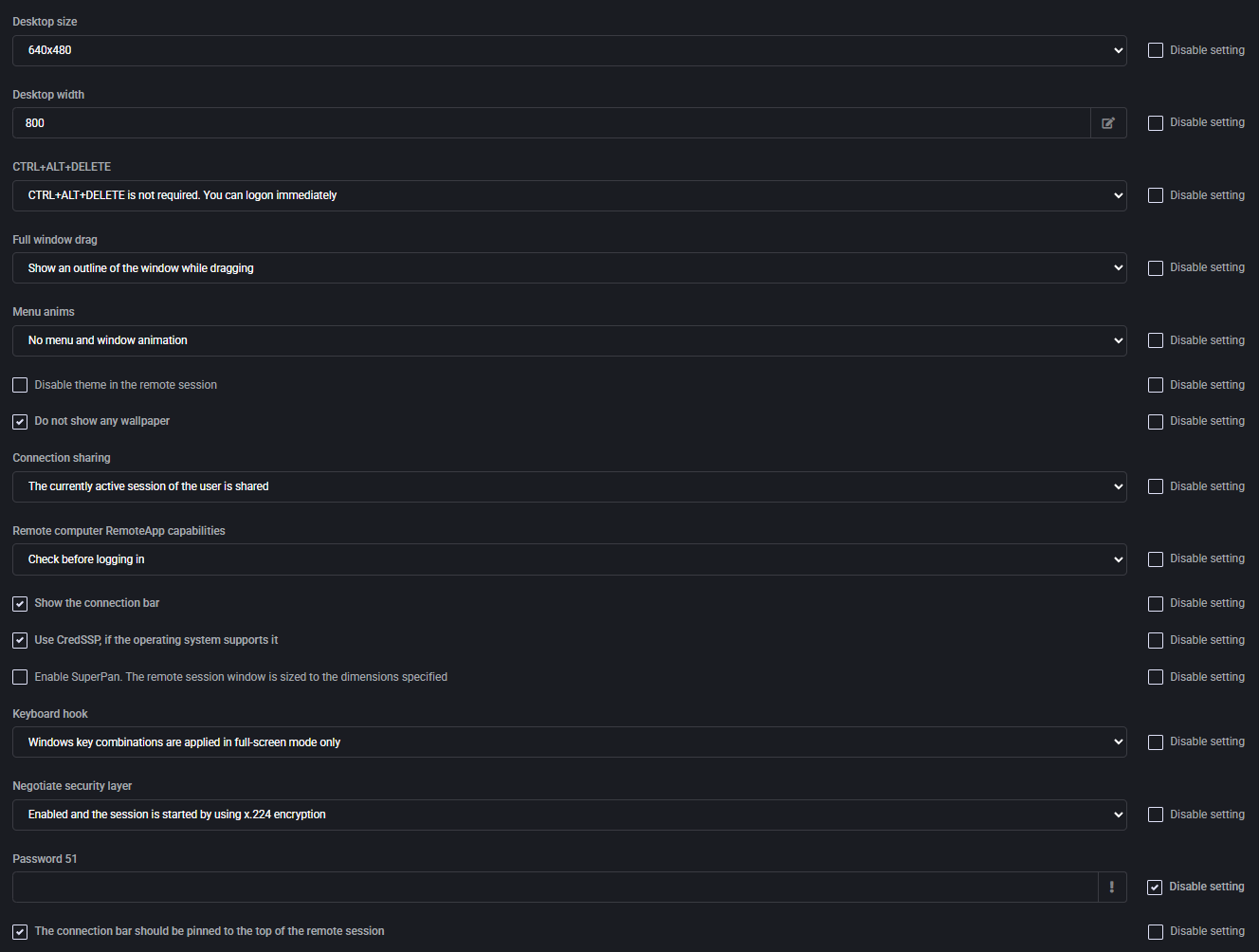
RDS Default Client Settings
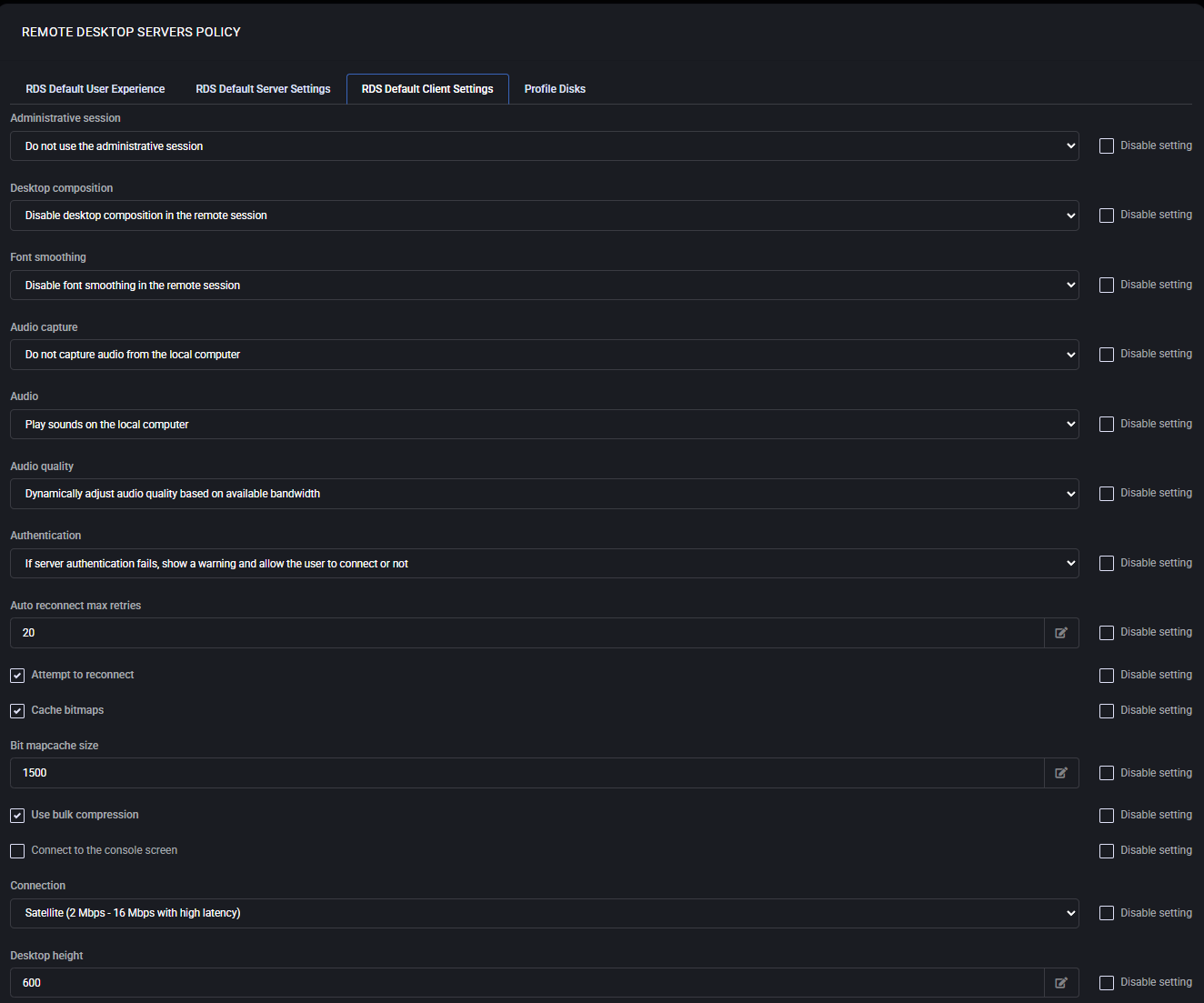
This section defines how Remote Desktop clients behave when connecting to the RDS server.
Administrators can configure display, audio, authentication, compression, and redirection options
to optimize both performance and user experience.
- Administrative Session:
Choose whether the administrative session is used during client connections.
- Desktop Composition:
Enable or disable desktop composition features in the remote session.
- Font Smoothing:
Controls whether ClearType font smoothing is applied in remote sessions.
- Audio Capture:
Configure if audio from the local device is captured in the remote session.
- Audio:
Decide if sounds play locally or remotely during the session.
- Audio Quality:
Dynamically adjust quality based on available bandwidth.
- Authentication:
Configure behavior if server authentication fails (e.g., warn user or block connection).
- Auto Reconnect Max Retries:
Define the maximum number of retries when reconnecting to a session.
- Attempt to Reconnect:
Allow client to auto-reconnect if the session drops unexpectedly.
- Cache Bitmaps:
Enable bitmap caching for performance optimization.
- Bitmap Cache Size:
Configure maximum size of bitmap cache in KB.
- Use Bulk Compression:
Enable or disable RDP bulk compression for network efficiency.
- Connect to Console Screen:
Allows direct connection to the console session instead of a standard RDP session.
- Connection Type:
Define connection speed (e.g., Satellite, LAN, Broadband), which adjusts bandwidth usage.
- Desktop Resolution (Height/Width/Size):
Predefine resolution values for the client desktop session.
- CTRL+ALT+DEL Requirement:
Configure whether secure sign-in is required.
- Full Window Drag:
Enable or disable full window rendering while dragging.
- Menu Animations:
Allow or disable UI menu animations.
- Disable Theme in Remote Session:
Prevents loading of themes and wallpapers to save bandwidth.
- Connection Sharing:
Determines if the current active session can be shared.
- RemoteApp Capabilities:
Configure whether to check RemoteApp support before login.
- Show Connection Bar:
Displays a floating connection bar during RDP sessions.
- Use CredSSP:
Enables Credential Security Support Provider if supported by the OS.
- Enable SuperPan:
Allows resizing session window beyond client resolution.
- Keyboard Hook:
Configures Windows key handling (local, remote, or fullscreen only).
- Negotiate Security Layer:
Defines whether to use TLS/SSL security for the connection.
- Password 51:
Stores encrypted password string for session login.
- Pin Connection Bar:
Ensures connection bar stays pinned on top of session.
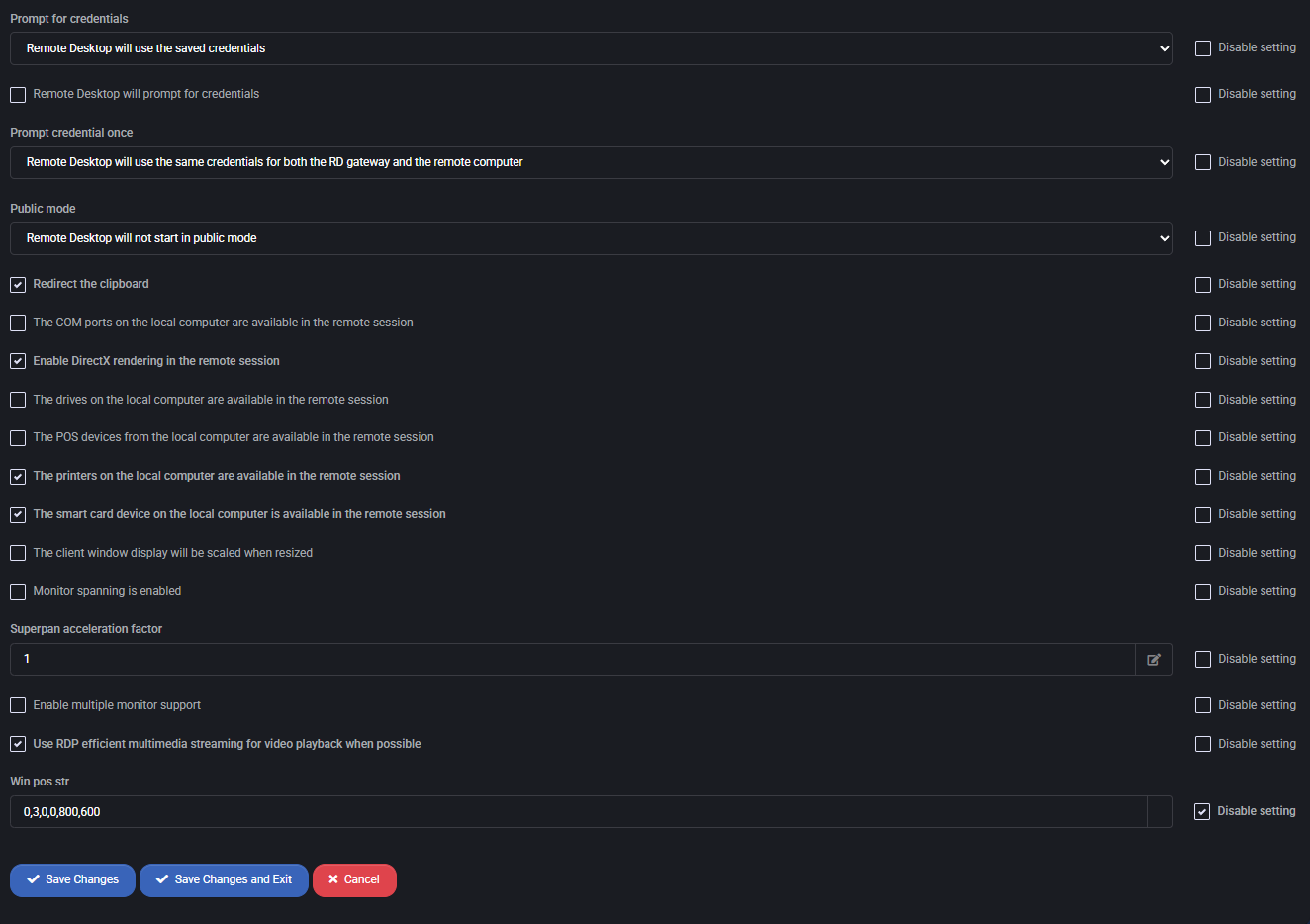
- Prompt for Credentials:
Configure if users must provide credentials at connection start.
- Prompt Credential Once:
Decide if the same credentials are used for both RD Gateway and remote host.
- Public Mode:
Configure if session should start in restricted “public” mode.
- Clipboard Redirection:
Allow or block clipboard sharing between client and remote session.
- Local Device Redirection:
Enable redirection of COM ports, printers, drives, smart cards, and POS devices.
- Enable DirectX Rendering:
Improves graphical performance by using DirectX acceleration in remote sessions.
- Client Window Scaling:
Scale client window dynamically when resized.
- Monitor Spanning:
Allow remote sessions to span across multiple monitors.
- SuperPan Acceleration Factor:
Adjust acceleration scaling for SuperPan window mode.
- Multiple Monitor Support:
Enable support for multiple monitors in remote sessions.
- RDP Multimedia Redirection:
Optimize audio/video playback using RDP multimedia extensions.
- Win Pos Str:
Defines exact coordinates and dimensions for RDP window placement.
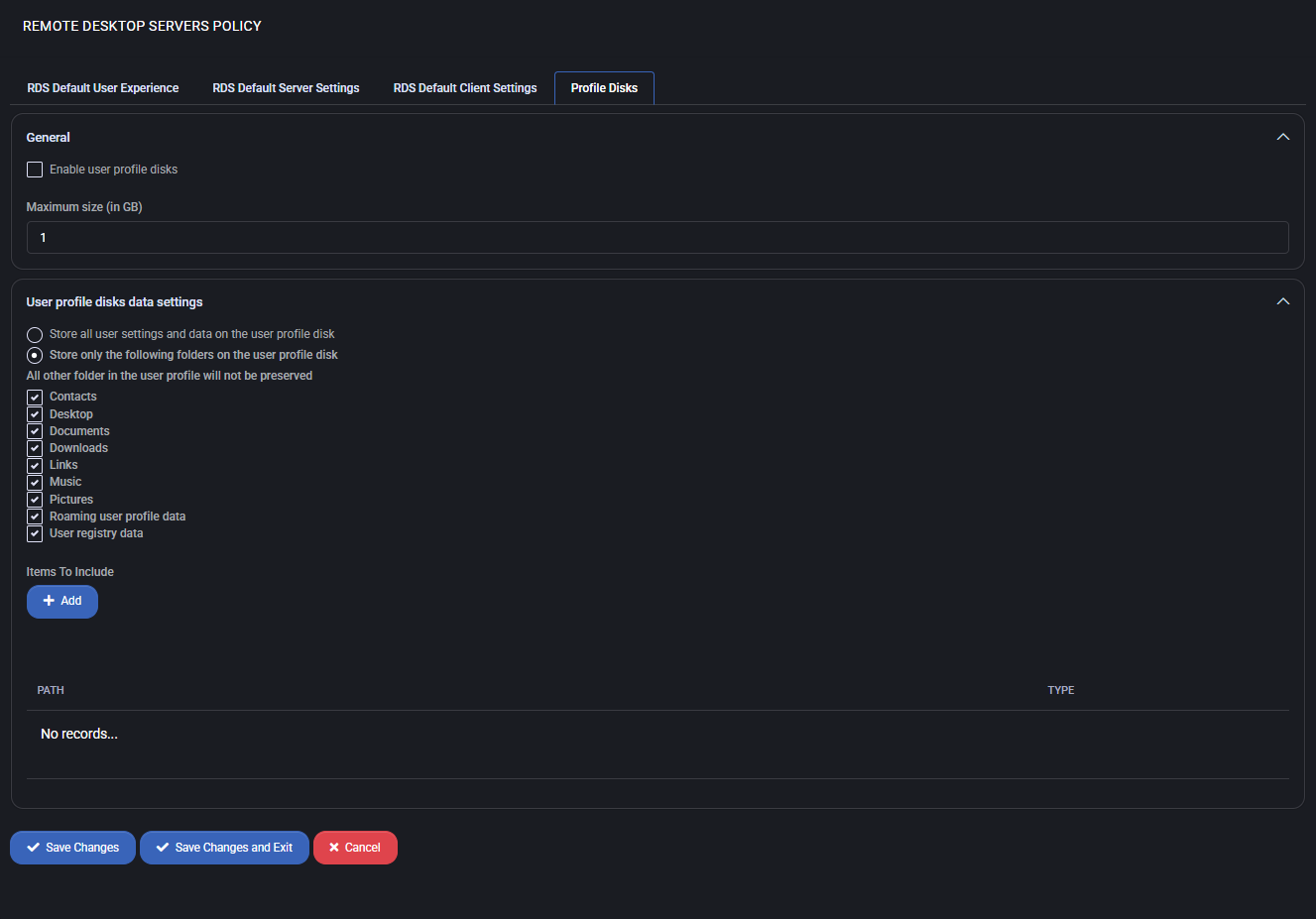
Profile Disks
This section allows administrators to configure user profile disks (UPDs) for Remote Desktop Sessions. UPDs store user profiles on a central location, enabling a consistent experience across multiple sessions while optimizing storage usage.
- Enable Profile Disks:
Determines whether profile disks are used for storing user profiles in RDS sessions.
- Disk Path:
Specifies the network share or folder path where profile disks will be stored.
- Disk Size (MB):
Sets the maximum allocated size per user disk. Proper sizing ensures smooth user experience while controlling storage costs.
- Include Folders:
Allows administrators to specify which folders inside the user profile should be redirected and stored on the UPD (e.g., Desktop, Documents, AppData).
- Exclude Folders:
Defines folders that should not be stored on the profile disk, preventing excessive growth and unnecessary sync.
Best Practices for Remote Desktop Servers Policy
When configuring RDS policies in MSPControl, follow these best practices to achieve a balance between security, performance, and user experience:
- Enforce Secure Authentication:
Always require TLS and Network Level Authentication to protect RDS logins from interception and brute-force attempts.
- Limit Idle and Disconnected Sessions:
Configure reasonable session timeouts (e.g., 4–8 hours for idle/disconnected sessions) to optimize server resource usage.
- Use Profile Disks Strategically:
Store only critical folders (Documents, Desktop, AppData) on profile disks and exclude temporary or large media folders to reduce storage overhead.
- Optimize User Experience:
Disable unnecessary features like animations, wallpapers, or theme loading to improve bandwidth efficiency for remote connections.
- Restrict Administrative Tools:
Remove access to cmd.exe, PowerShell, and Task Manager for regular users to reduce the risk of privilege escalation.
- Redirect Devices Carefully:
Enable only necessary redirections (printers, drives, smart cards) to balance usability and security. Avoid redirecting COM ports or POS devices unless explicitly required.
- Monitor Storage & Disk Usage:
Regularly audit UPD size and usage thresholds to prevent uncontrolled growth and potential downtime caused by full disks.
- Use Group-Specific Policies:
Apply different settings for administrators vs. end-users. For example, admins may retain broader access, while users are locked into restricted sessions.













