Database Policies
The Database Policies section in MSPControl allows administrators to define how SQL-based services are provisioned and managed. These policies help standardize the creation of databases and users, enforce secure password policies, and define backup capabilities across two major database engines: Microsoft SQL Server and MySQL.
Each sub-policy includes options for name formatting, allowed symbols, character limits, password complexity, and more. This centralized control ensures consistent and secure database provisioning for all hosting spaces managed through MSPControl.
Table of Contents
MS SQL Policy
The MS SQL Policy section allows administrators to configure default behavior, naming conventions, and password security requirements for Microsoft SQL databases and users created within MSPControl. These settings help ensure secure, consistent provisioning across all hosting environments.
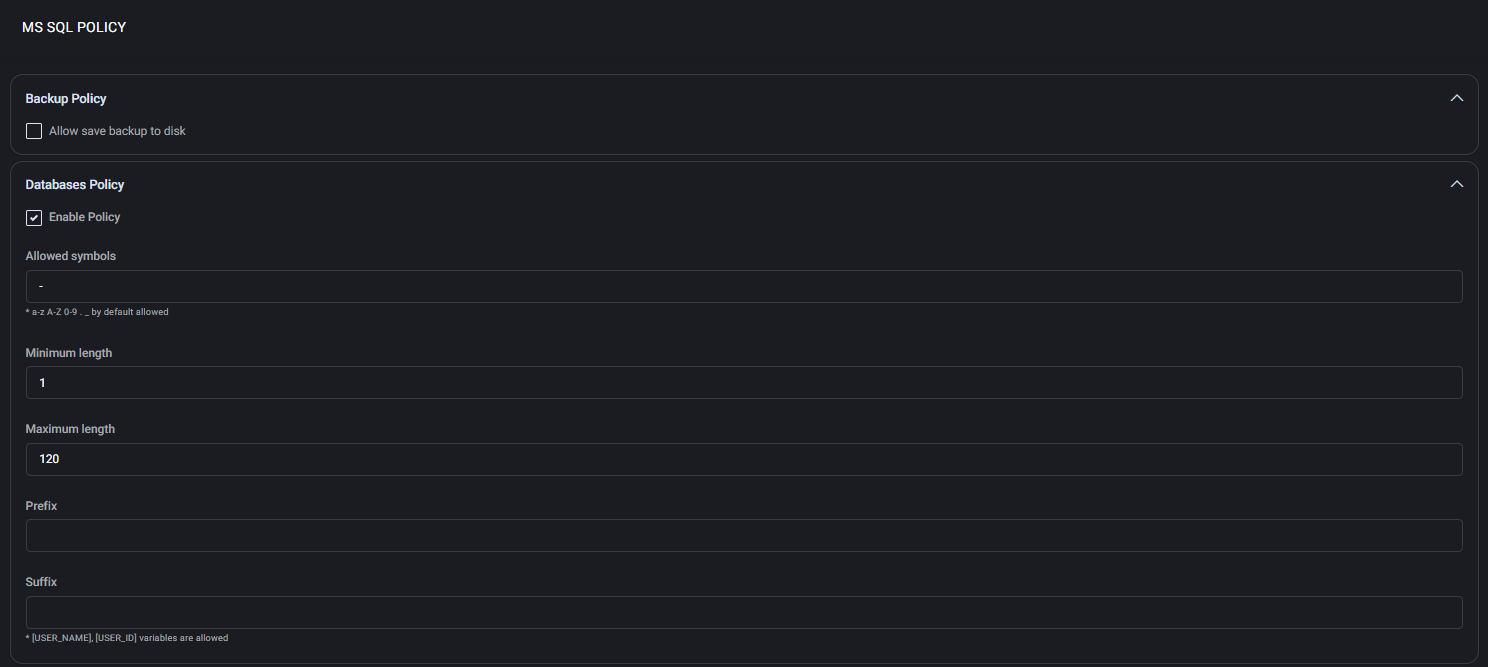
Backup Policy
Defines whether end users are allowed to store database backups directly on the disk of the SQL server.
- Allow save backup to disk: Enables manual SQL backup creation and storage on the physical disk. Disable this if backups should only be handled by automated processes or external backup systems.
Databases Policy
This subsection defines the formatting rules for SQL database names created by customers.
- Enable Policy: Turns on all validation rules defined in this block.
- Allowed Symbols: Allows additional characters in names. By default, only
a-z, A-Z, 0-9, underscore _, and period . are allowed. In this policy, hyphen - is additionally permitted.
- Minimum length: The minimum number of characters required in a database name (e.g., 1).
- Maximum length: The maximum number of characters allowed (up to 120).
- Prefix / Suffix: Optional fixed strings or tokens (like
[USER_NAME], [USER_ID]) that will be prepended or appended to the database name during creation.
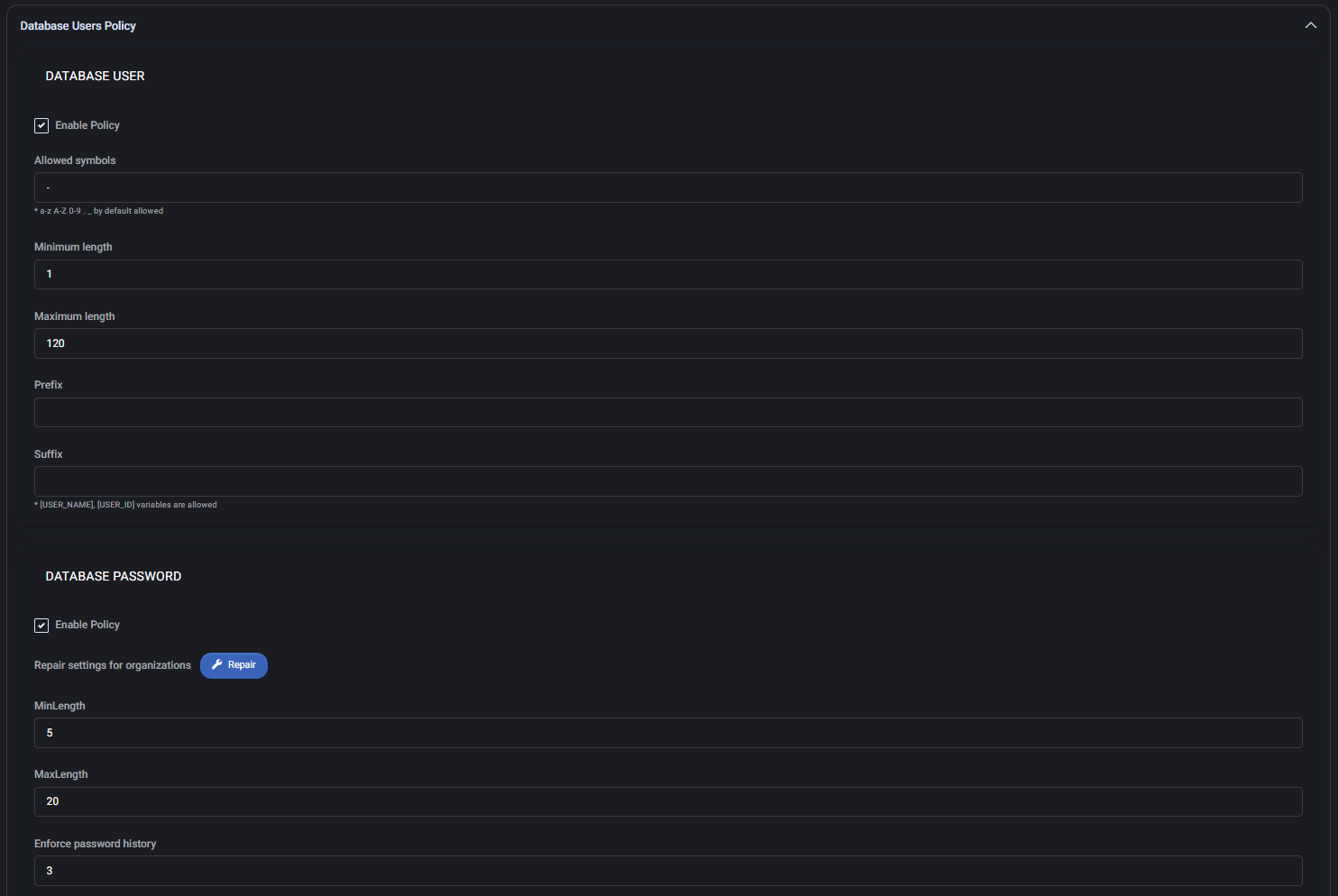
Database Users Policy
This policy defines the naming and password rules for Microsoft SQL database users created under a hosting space.
Database User
- Enable Policy: Enables validation for username format.
- Allowed Symbols: Additional characters allowed beyond the default alphanumeric set. In this case, the policy includes
- and ..
- Minimum / Maximum Length: Username must be between 1 and 120 characters.
- Prefix / Suffix: Optional fields for automated naming structure, which can include dynamic tokens such as
[USER_NAME].
Database Password
- Enable Policy: Turns on all password rules for SQL user accounts.
- Repair settings for organizations: Reapplies password policies to existing orgs if they are out of sync.
- MinLength / MaxLength: Password must be between 5 and 20 characters.
- Enforce password history: Prevents reuse of the last 3 passwords.
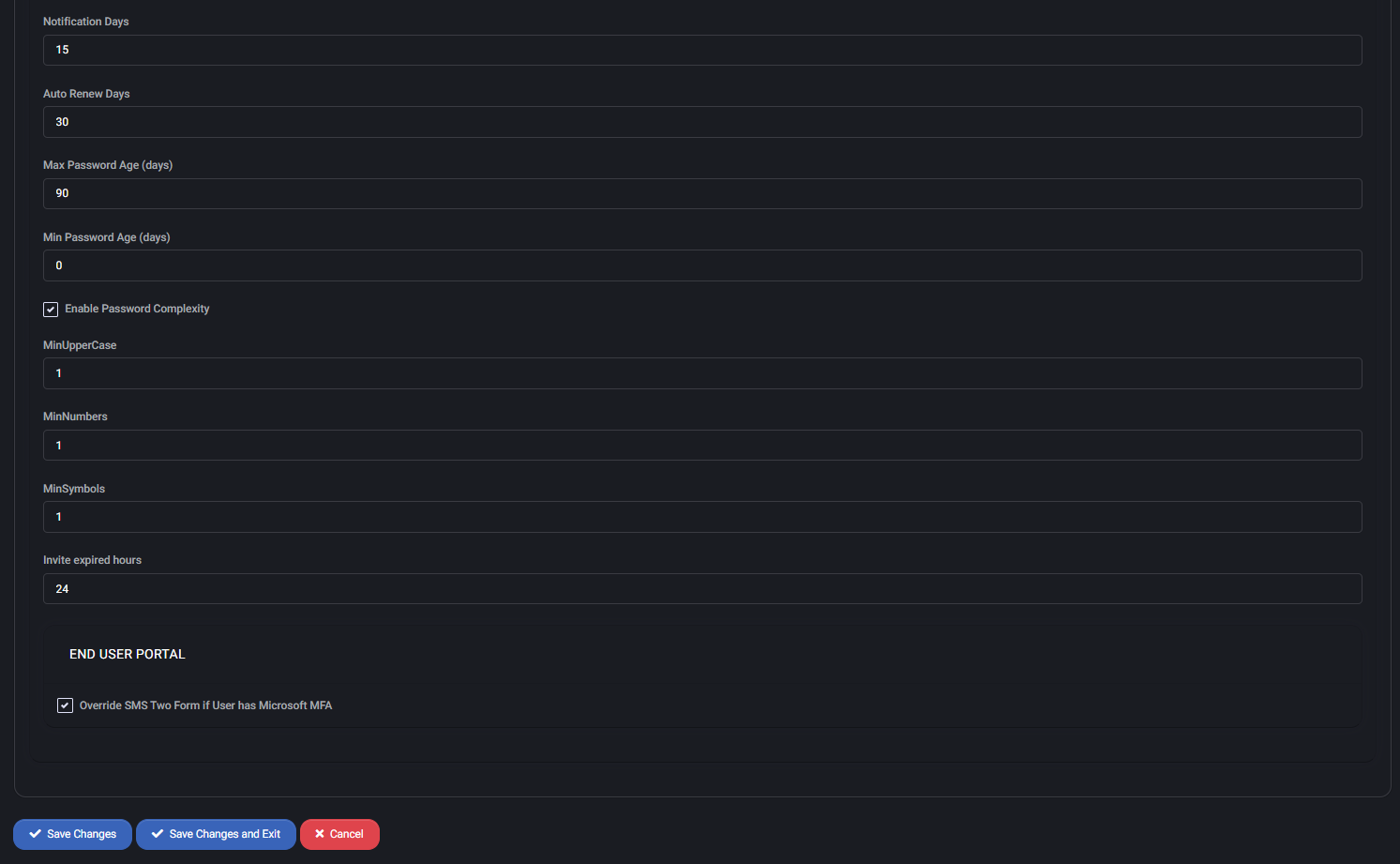
- Notification Days: Sends warning 15 days before password expiration.
- Auto Renew Days: Password will be automatically rotated every 30 days.
- Max Password Age: Passwords expire after 90 days.
- Min Password Age: Password can be changed immediately (value is 0).
- Enable Password Complexity: Requires inclusion of uppercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- MinUpperCase / MinNumbers / MinSymbols: At least 1 of each is required.
- Invite expired hours: Password invite links expire after 24 hours.
End User Portal
- Override SMS Two Form if User has Microsoft MFA: If enabled, MSPControl will skip its own SMS-based 2FA enforcement when Microsoft MFA is already active for the user. Helps prevent double-authentication conflicts.
MySQL Policy
This policy governs MySQL database configuration, including backup options, naming standards, and user/password rules. It mirrors many settings from the MS SQL Policy but is configured independently.
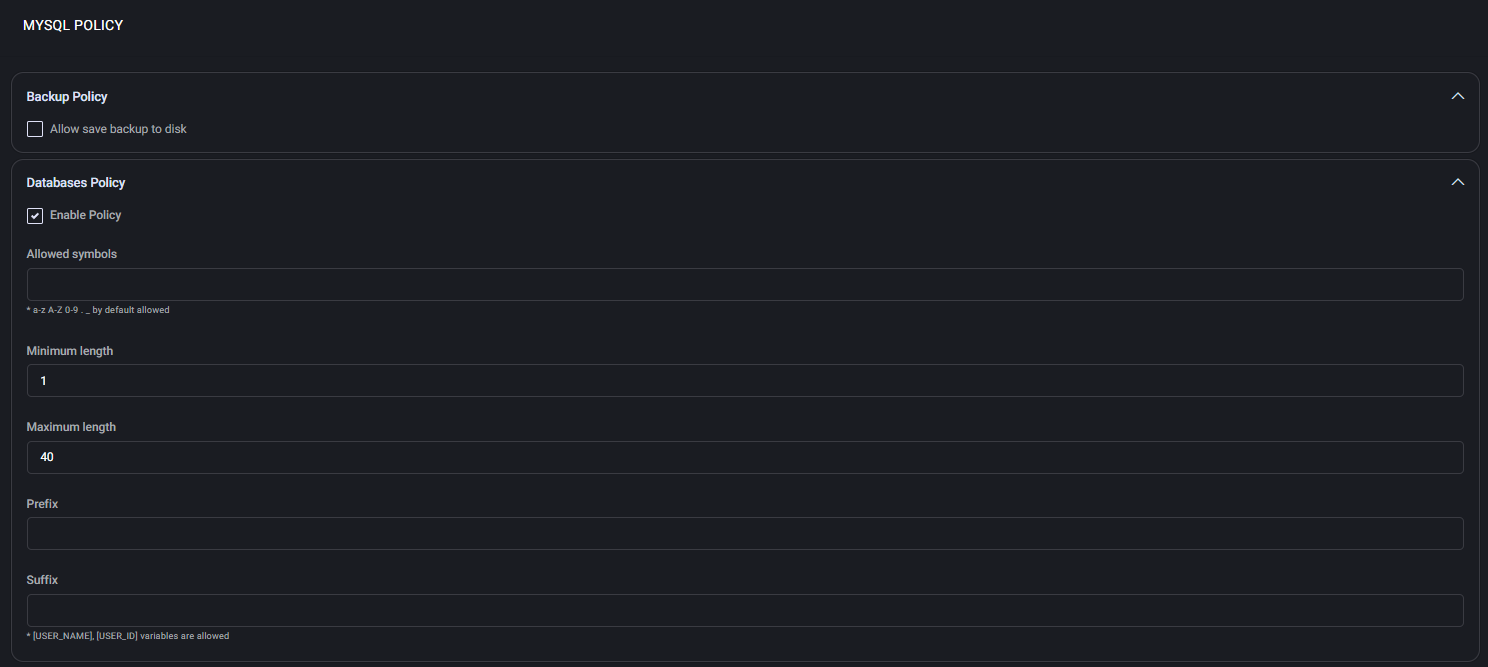
Backup Policy
Allow save backup to disk:
Enables or disables the ability to create and download local backups of MySQL databases.
Databases Policy
Enable Policy: Activates the rules defined in this section for MySQL database names.
- Allowed symbols: Additional characters allowed in names beyond the standard set (a-z, A-Z, 0-9, “_”).
- Minimum length: Minimum number of characters required in a database name (e.g., 1).
- Maximum length: Maximum number of characters allowed (e.g., 40).
- Prefix / Suffix: Optional values that will be prepended or appended to the database name. You can use variables like
[USER_NAME] and [USER_ID] for dynamic generation.
Database Users Policy
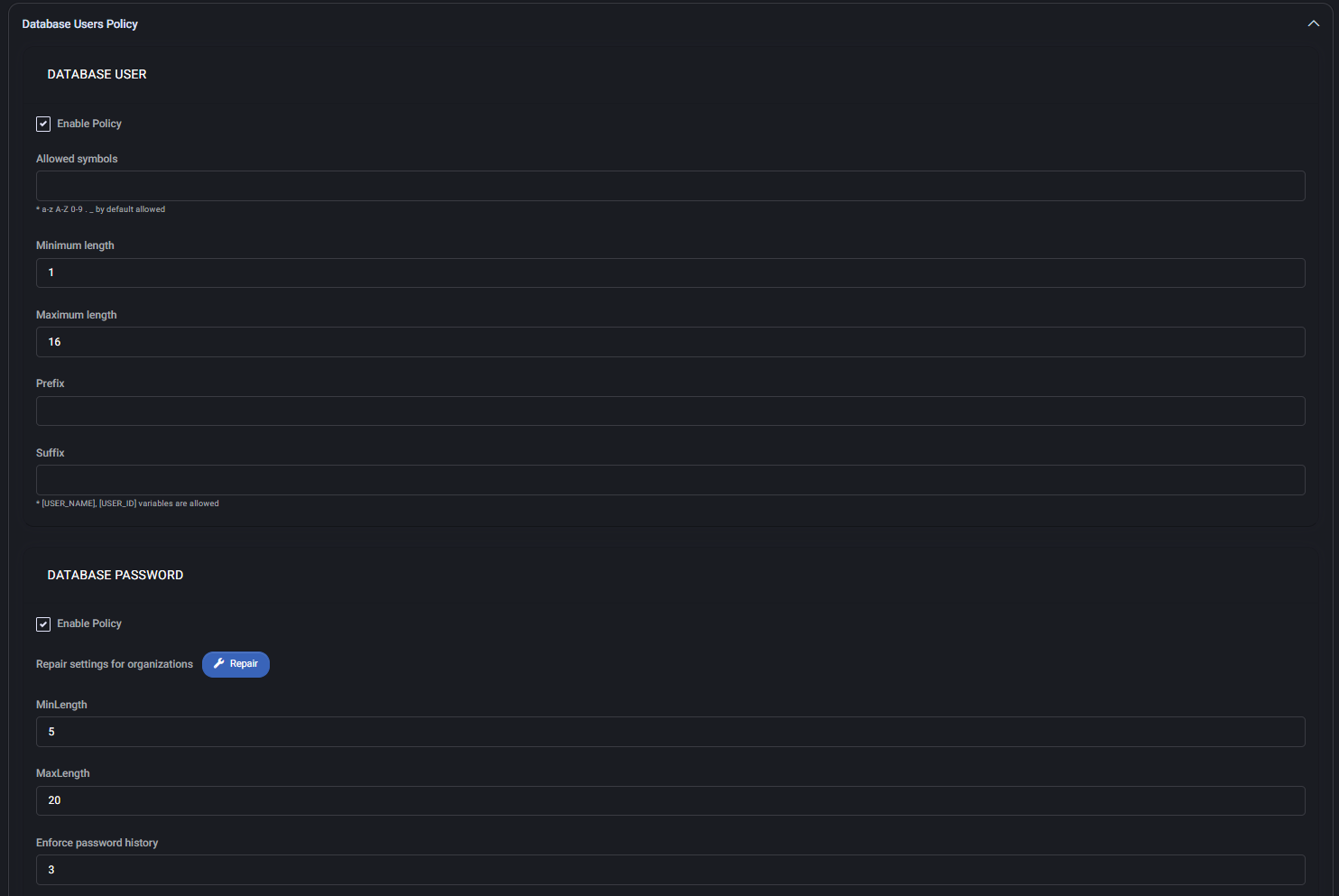
Database User
- Enable Policy: When enabled, all settings defined here will apply to user account creation.
- Allowed symbols: Restrict which additional characters can be used in usernames beyond the default set.
- Minimum length: Required minimum number of characters (e.g., 1).
- Maximum length: Required maximum number of characters (e.g., 16).
- Prefix / Suffix: Automatically append defined values to each username. Variables like
[USER_NAME] and [USER_ID] are supported.
Database Password
- Enable Policy: Enables the enforcement of the password rules listed below.
- Repair settings for organizations: The Repair button allows administrators to reset password settings for all organizations to match this policy.
- MinLength / MaxLength: Define the password character limits (e.g., between 5 and 20 characters).
- Enforce password history: Prevents users from reusing the last 3 passwords.
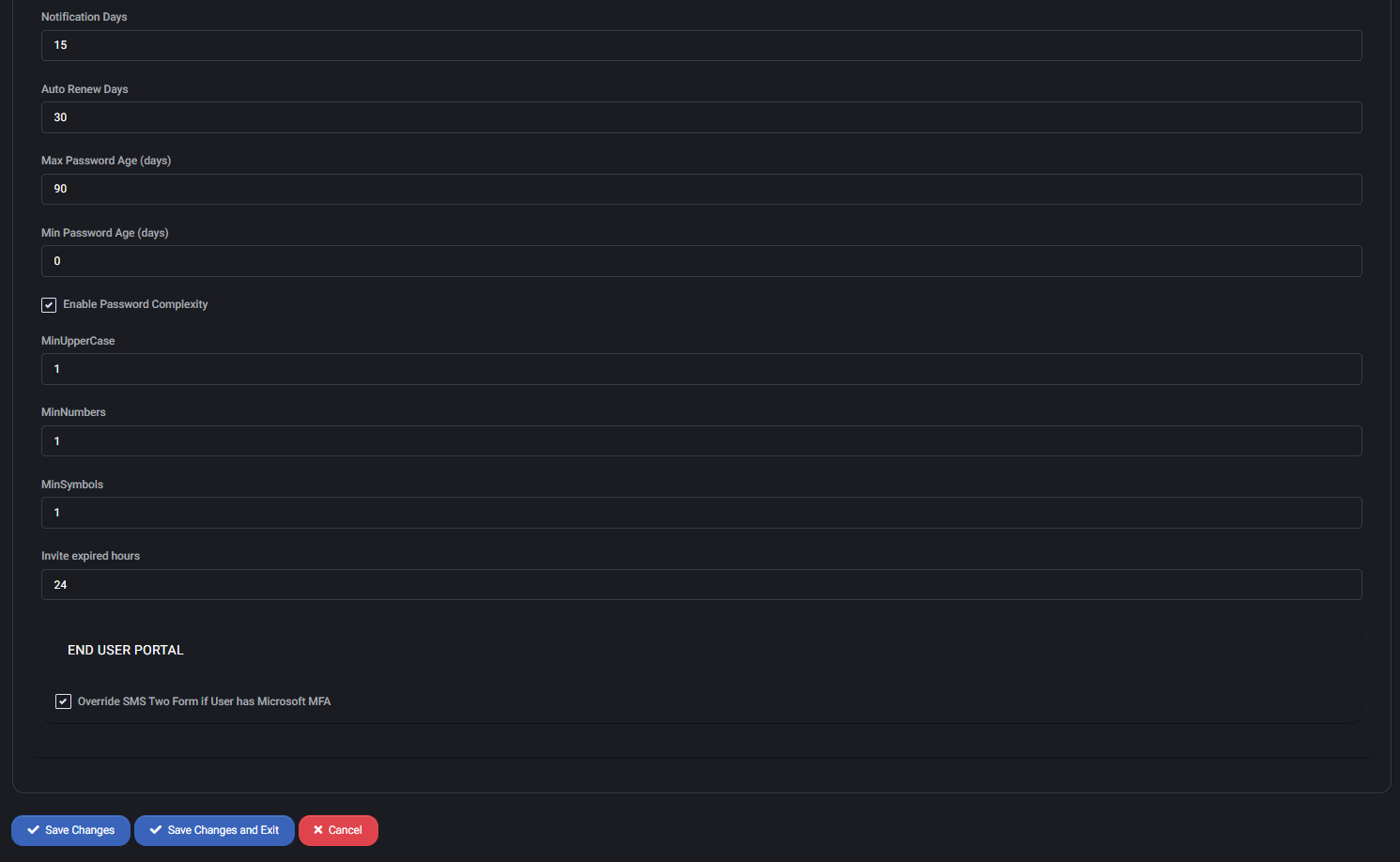
- Notification Days / Auto Renew Days: Controls when users are notified of upcoming expiration and when automatic renewals are triggered (e.g., 15 and 30 days).
- Max Password Age / Min Password Age: Sets the allowable lifetime of a password (e.g., 90 days max, 0 min).
- Enable Password Complexity: Enforces complexity rules if enabled, including:
- MinUpperCase: Required number of uppercase letters (e.g., 1)
- MinNumbers: Required number of numeric characters (e.g., 1)
- MinSymbols: Required number of special characters (e.g., 1)
- Invite expired hours: Defines how long user invites remain valid (e.g., 24 hours).
End User Portal
- Override SMS Two Form if User has Microsoft MFA: Automatically disables SMS-based two-factor authentication for users already protected by Microsoft MFA.








