Audit Log
The Audit Log in MSPControl provides a comprehensive record of system events, user actions, and administrative changes. By reviewing these entries, administrators can troubleshoot issues, monitor activity, and maintain security or compliance standards.
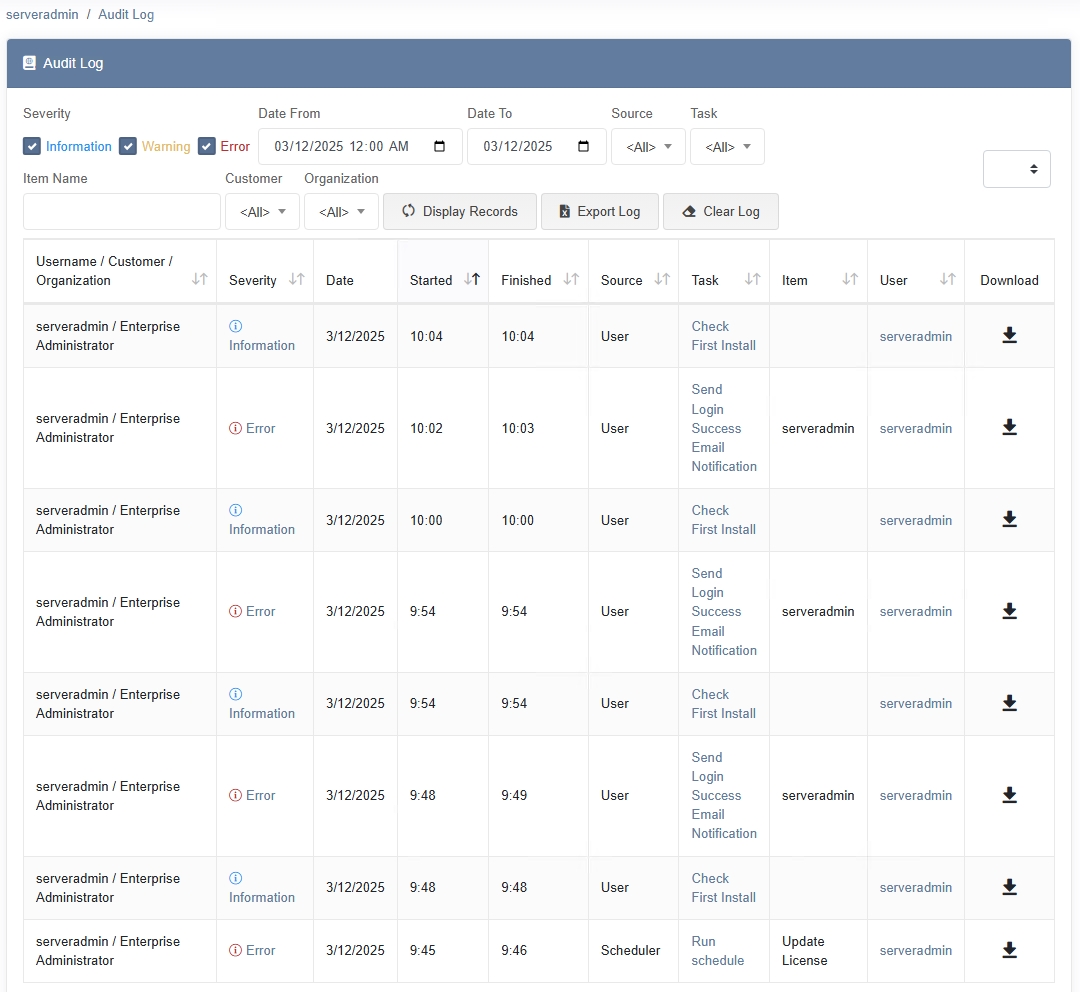
Overview
Each entry in the Audit Log typically includes the following columns:
- Severity – Categorizes the event as Information, Warning, or Error.
- Date – The date when the log entry was created.
- Started / Finished – Timestamp indicating when a particular action began and ended (if applicable).
- Source – The originating component or module (e.g., System, Scheduler, User).
- Task – Identifies the specific task or action (e.g., Change password, Update License).
- User – Which user or account performed the action. Often shows serveradmin for system-level operations.
- Item Name – Additional context or identifier for the action (e.g., Domain Name, Service ID).
- Customer / Organization – For multi-tenant environments, indicates which customer or organization the event pertains to.
- Download – Some events may include logs or output data you can download for deeper analysis.
Filtering and Searching
You can refine the displayed log entries using the following filters:
- Date Range – Specify a start and end date to see events within a particular window.
- Severity – Filter by Information, Warning, or Error to focus on relevant events.
- Source – Limit results to events from a particular component (e.g., Scheduler, User, System).
- Task – Narrow entries to a specific task name (e.g., Get Latest Version, Check First Install).
Click Display Records to apply your chosen filters and refresh the log results.
Additional Actions
- Export Log – Generates a downloadable file (often in CSV format) containing the filtered log entries, allowing you to archive or analyze them externally.
- Clear Log – Permanently removes the current log entries from MSPControl. Use with caution, as clearing logs can impact audit history and forensics.
Best Practices
- Regular Reviews – Periodically check the Audit Log for unusual activity or repeated errors.
- Export Before Clearing – If you plan to clear the log, consider exporting it first to maintain a historical record for audits or compliance.
- Combine Filters – Use multiple filters (e.g., severity + source + task) to quickly pinpoint specific events or troubleshoot issues more efficiently.
- Retain Critical Logs – Align log retention policies with your organization’s security and compliance requirements.



